Active Control of Automobile Cabin Noise with Conventional and Advanced Speakers by Jerome Couche Committee Chairman: Chris R. Fuller, Mechanical Engineering (ABSTRACT) Recently much research has focused on the control of enclosed sound fields, particularly in automobiles. Both Active Noise Control (ANC) and Active Structural Acoustic Control This thesis contains material from 2 papers published in the following peer-reviewed tier 1 journals and 2 papers published in the following conference proceedings where I was the first author. Chapter 3 is published as V. Belyi and W. S. Gan, “Psychoacoustic subband active noise control algorithm,” in Proceedings - 9th Asia-Pacific Signal and Active Voice Control: An Implementation of Active Noise Control for Canceling Speech Except where reference is made to the work of others, the work described in this thesis is my own or was done in collaboration with my advisor. This thesis does not include proprietary or classified information. Christopher Rose Certificate of Approval: Vishwani Agrawal
Noise Control through Active Noise Cancellation Technique in Mines - ethesis
edu no longer supports Internet Explorer. To browse Academia. edu active noise control thesis the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser.
Log In with Facebook Log In with Google Sign Up with Apple, active noise control thesis. Remember me on this computer. Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. Need an account? Click here to sign up. Download Free PDF. Stability analysis of adaptation process in FxLMS-based active noise control Iman Ardekani. Download PDF Download Full PDF Package This paper.
A short summary of this paper. Download PDF. Download Full PDF Package. Translate PDF. nz ResearchSpace Auckland Copyright Statement The digital copy of this thesis is protected by the Copyright Act New Zealand. This thesis may be consulted by you, provided you comply with the provisions of the Act and the following conditions of use: x Any use you make of these documents or images must be for research or private study purposes only, and you may not make them available to any other person.
x Authors control the copyright of their thesis. You will recognise the author's right to be identified as the author of this thesis, and due acknowledgement will be made to the author where appropriate.
x You will obtain the author's permission before publishing any material from their thesis. To request permissions please use the Feedback form on our webpage.
Note : Masters Theses The digital copy of a masters thesis is as submitted for examination and contains no corrections. The print copy, usually available in the University Library, may contain corrections made by hand, active noise control thesis, which have been requested by the supervisor.
Stability Analysis of Adaptation Process in FxLMS-Based Active Noise Control Iman Tabatabaei Ardekani Supervisor: Dr. Waleed H. Abdulla A thesis submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Electrical and Electronic Engineering, active noise control thesis, The University of Auckland, New Zealand.
blank blank To my family. Acknowledgements First and foremost, active noise control thesis, I would like to express my sincere gratitude to Dr, active noise control thesis. Abdulla, who was my supervisor and mentor over the past 4 years. His active noise control thesis, expertise, support, guidance and encouragements have been invaluable and appreciated. Also, I would like to thank A. Sing Active noise control thesis Nguang who was my co-supervisor and guided me to conduct this research.
I would like to thank the examiners of this thesis, Dr. Paul Teal and Professor Yoshinobu Kajikawa, for their valuable comments, which definitely improved the quality of this work.
Last but not least, my deepest thanks to my parents and family for their continuous support throughout these years. Their understanding and support encouraged me to do my best in this Ph. D research. Also, my special thank goes to my friend, Ramin Vali, for sharing his expertise.
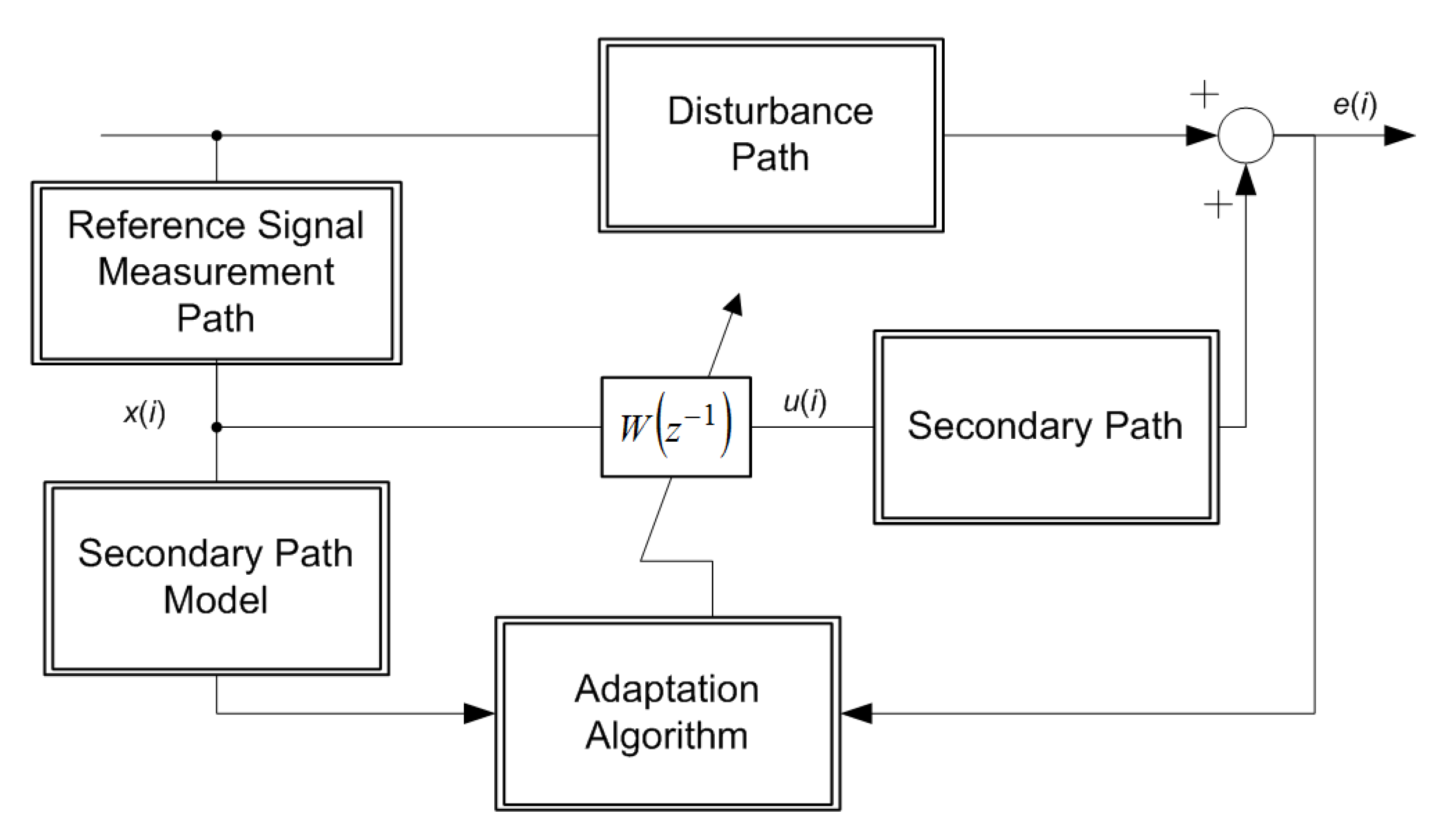
Generally, this algorithm is used in system identification problems in which a physical channel, called the secondary path, follows the adaptive filter. The FxLMS algorithm compensates for the secondary path effect by filtering the input signal training data sequence using an available estimate of the secondary path, called the secondary path model.
However, this filtering causes the analytical model of the adaptation process to become highly complex. Because of this complexity, this model has to be simplified when it is desired to derive closed-form expressions for formulating different behaviours of the adaptation process. Usually, this simplification has been carried out by using unrealistic assumptions of pure delay secondary paths, broad-band acoustic noise, and perfect secondary path models.
The first contribution of this thesis is the derivation of a set of closed-from mathematical expressions for formulating behaviours of Active noise control thesis ANC systems in steady-state and transient conditions.
This derivation is carried out without using any simplifying assumption regarding the secondary path, active noise control thesis. Con- sequently, the obtained expressions extend the available knowledge on FxLMS-based ANC systems. The second contribution is formulating influences of acoustic noise band-width on the newly-derived expressions. In the analysis of ANC systems with stochastic noise, it is usual to assume a broad-band acoustic noise with a flat frequency spectrum which is usually referred to as a white signalin order to avoid mathematical complexity.
However, even if the acoustic noise active noise control thesis a flat spectrum over a wide frequency range, the signal picked up and fed to the ANC system is required to be processed with a sampling frequency higher than the maximum frequency of the acoustic noise. For this reason, a realistic active noise control thesis signal can only have a flat spectrum over a active noise control thesis band-width.
The third contribution is investigating influences of secondary path models on the newly-derived expres- sions. Usually, it is acceptable to assume a perfectly-accurate secondary path model; however, in order to generalise the obtained closed-form expressions, this assumption is also removed in this thesis. Con- sequently, the final closed-form expressions, proposed in this thesis, active noise control thesis, can apply to a relatively general case with an arbitrary secondary path, an acoustic noise with an arbitrary band-width, active noise control thesis, and an arbitrary imperfect secondary path model.
Another contribution of this thesis is determining trajectories of the poles of the FxLMS adaptation process in the z-plane. This investigation leads to find the FxLMS adaptation process root locus. A mechanism for localising this pole is then proposed in this thesis, resulting in a novel ANC algorithm, called the Filtered Weight FxLMS. In addition to several numerical analyses and computer simulations, a FPGA-based ANC setup, de- veloped for this research, is used to study the validity of the theoretical results obtained in this thesis.
This setup is developed by using a flexible FPGA programming structure which can be used for the im- plementation of other ANC algorithms. Different experiments with this setup confirms the validity of the theoretical results proposed in this thesis. Publications List Most of the research results, obtained in this thesis, have been peer-reviewed and published in 11 different ISI journals and international conferences proceedings.
The list of these publications can be viewed in the following: 1. Tabatabaei Ardekani and W. Contents Front Matter i Abstract. v Publications. vii Contents. ix List of Figures. xiv 1 Introduction 1 1. iii A. These silencers are valued for their global noise attenuation; however, they are relatively bulky, costly and ineffective for low frequency noise.
To overcome these problems, Active Noise Control ANCin which an electro-acoustic system is responsible to create a local silence zone, has received considerable interest. The first patent on active noise control was granted to Paul Leug, in [1]. Figure 1. However, all of these analog ANC devices are not able to adapt to changing characteristics of the noise to be cancelled nor to changing environmental conditions.
This is because adaptive signal processing techniques cannot be realised by using analog electronic technology. Only with the advent of digital technology did the realisation of adaptive ANC systems become possible. The theory of adaptive ANC, in which an adaptation algorithm automatically adjusts the ANC device, was established by Widrow in [6]; however the most significant progresses on this subject has been reported in the last two decades [7, 8].
In this chapter, the theory behind adaptive ANC is elaborated, followed by a literature review on signal processing techniques used in design and implementation of adaptive ANC devices. Shortcomings of available relevant work are discussed, based on which the main outstanding problems to be dealt with in this thesis are defined. Based on the linearity of this process, the active noise control thesis of interference between sound waves, upon which the ANC theory is established, is then discussed, active noise control thesis.
The acoustic pressure is defined as the local deviation from the ambient atmospheric pressure1 caused by a sound wave. This scalar quantity, which can be directly measured using a micro- phone in air or a hydrophone in water, is the force N of sound on a surface area m2 perpendicular to the direction of the sound.
Therefore, based on the linearity of the acoustic wave propagation process, the net acoustic pressure at position x, y, z and discrete time index n caused by two or more sound sources, can be expressed as the algebraic sum of the acoustic pressures, caused by each sound source acting individually.
For formulating this phenomenon, let us assume that there are only two sound sources in the ambient. In this case, Eq. The interaction of these two sound waves at a given point x0y0z0 and time index n, is called the constructive interference if the absolute value of p x0y0z0n is equal or greater than the absolute values of p1 x0y0z0n and p2 x0y0z0n.
Otherwise, the active noise control thesis is called the destructive interference. This definition can be extended for a general case with an arbitrary number of sound sources. The phenomenon of destructive interference is the basis for the creation of a silence zone by ANC devices.
Also, it is shown that this mechanism should be precisely driven by a digital electronic control system. This situation is illustrated in Figure 1. Zs xsyszs is the position of a desired silence zone in three-dimensional space. eac n is the net acoustic pressure at Zs : eac np xsyszsn 1. dac n is the acoustic pressure at Zs caused by all the existing noise sources: dac npd xsactive noise control thesis, yszsn 1. d˜ac n is the acoustic pressure at Zs caused by the anti-noise control source: deac npd˜ xsyszsn 1.
The relation between the active noise control thesis and output of this mechanism is shown in Figure 1. According to this figure, the input of this mechanism is the control acoustic pressure at Zs caused by the anti-noise source, the disturbance signal is the unwanted acoustic pressure at Zsand the output signal is the net acoustic pressure at Zs.
The ANC physical mechanism generates the output signal as the summation of the input and disturbance signals. From Eq.
Listen As Active Noise Cancellation Makes Car Interiors 90% More Silent
, time: 0:56
This thesis deals with development of efficient methods for global active noise control (ANC) in vibro-acoustic cavities, such as automotive vehicles, aircrafts and other transportation equipment, under the presence of both the acoustic and structural disturbances ACTIVE CONTROL OF AUTOMOBILE CABIN NOISE WITH CONVENTIONAL AND ADVANCED SPEAKERS by Jerome Couche Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE in Mechanical Engineering APPROVED: Dr. Chris R. Fuller, Chairman It might seem impossible to you that all custom-written essays, research papers, Thesis On Active Noise Control speeches, book reviews, and other custom task completed by our writers are both Thesis On Active Noise Control of high quality and cheap. It is surprising, but we do have some tricks to lower prices without hindering quality
No comments:
Post a Comment